
To learn more about the income statement, see Income Statement Outline. The 500 year-old accounting system where every transaction is recorded into at least two accounts. We also allow you to split your payment across 2 separate credit card transactions or send a payment link email to another person on your behalf. If splitting your payment into 2 transactions, a minimum payment of $350 is required for the first transaction. Liabilities are presented as line items, subtotaled, and totaled on the balance sheet. Everything listed is an item that the company has control over and can use to run the business.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- A liability is any money that a company owes to outside parties, from bills it has to pay to suppliers to interest on bonds issued to creditors to rent, utilities and salaries.
- It ensures accuracy in recording financial transactions and ensures that the balance sheet is balanced.
- The decrease to equity as a result of the expense affects three statements.
- Cash Equivalents are also lumped under this line item and include assets that have short-term maturities under three months or assets that the company can liquidate on short notice, such as marketable securities.
- Current assets and liabilities can be converted into cash within one year.
Debits and Credits are the words used to reflect this double-sided nature of financial transactions. For example, imagine that a business’s Total Assets increased by $500. This change must be offset by a $500 increase in Total Liabilities or Total Equity. Along with Equity, they make up the other side of the Accounting Equation. It can be sold at a later date to raise cash or reserved to repel a hostile takeover.
Step 3 of 3
A company will be able to quickly assess whether it has borrowed too much money, whether the assets it owns are not liquid enough, or whether it has enough cash on hand to meet accounting equation assets liabilities equity current demands. As you can see, all of these transactions always balance out the accounting equation. This equation holds true for all business activities and transactions.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
As transactions occur within a business, the amounts of assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity change. That part of the accounting system which contains the balance sheet and income statement accounts used for recording transactions. Liabilities and equity make up the right side of the balance sheet and cover the financial side of the company.
Income and retained earnings

The company has yet to provide the service, so it has not fulfilled the obligation yet. According to the revenue recognition principle, the company cannot recognize that revenue until it meets this performance obligation or in other words provides the service. Therefore, the company has a liability to the customer to provide the service and must record the liability as unearned revenue.
- The income statement would see an increase to revenues, changing net income (loss).
- For example, if a stock is worth $30 in January and $50 in March, the net change is $20.
- If the company takes $8,000 from investors, its assets will increase by that amount, as will its shareholder equity.
- Owners’ equity typically refers to partnerships (a business owned by two or more individuals).
- Property, Plant, and Equipment (also known as PP&E) capture the company’s tangible fixed assets.
- The total shareholder’s equity section reports common stock value, retained earnings, and accumulated other comprehensive income.
An asset can be cash or something that has monetary value such as inventory, furniture, equipment etc. while liabilities are debts that need to be paid in the future. For example, if you have a house then that is an asset for you but it is also a liability because it needs to be paid off in the future. This transaction would reduce cash by $9,500 and accounts payable by $10,000.

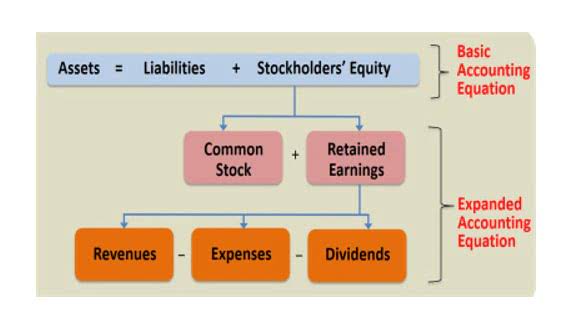
However, calculating stockholders’ equity can be a complex and daunting task for non-accountants. In this article, we will break down the process of calculating stockholders’ equity on the balance sheet and provide practical examples to help you understand this essential financial concept. The accounting equation is often expressed as an accounting formula and states that the sum of liabilities and equity is always equivalent to the total assets https://www.bookstime.com/articles/royalties-accounting of the organization. It is the fundamental foundation of accounting that ensures financial statement accuracy. If the left side of the accounting equation (total assets) increases or decreases, the right side (liabilities and equity) also changes in the same direction to balance the equation. The accounting equation asserts that the value of all assets in a business is always equal to the sum of its liabilities and the owner’s equity.
Owner’s equity formula

Shareholders’ equity is the total value of the company expressed in dollars. Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them. Assets represent the valuable resources controlled by a company, while liabilities represent its obligations. Both liabilities and shareholders’ equity represent how the assets of a company are financed.
This contributed amount represents the investors’ equity interest in the firm. Under the model of a private limited company, the firm may keep contributed capital as long as it remains in business. If it liquidates, whether through a decision of the owners or through a bankruptcy process, the owners have a residual claim on the firm’s eventual equity. If the equity is negative (a deficit) then the unpaid creditors bear loss and the owners’ claim is void. The purpose of the accounting equation is that it lays the framework for the accounting processes and ensures integrity in financial transaction recording.










